Dénutrition dans les soins de santé
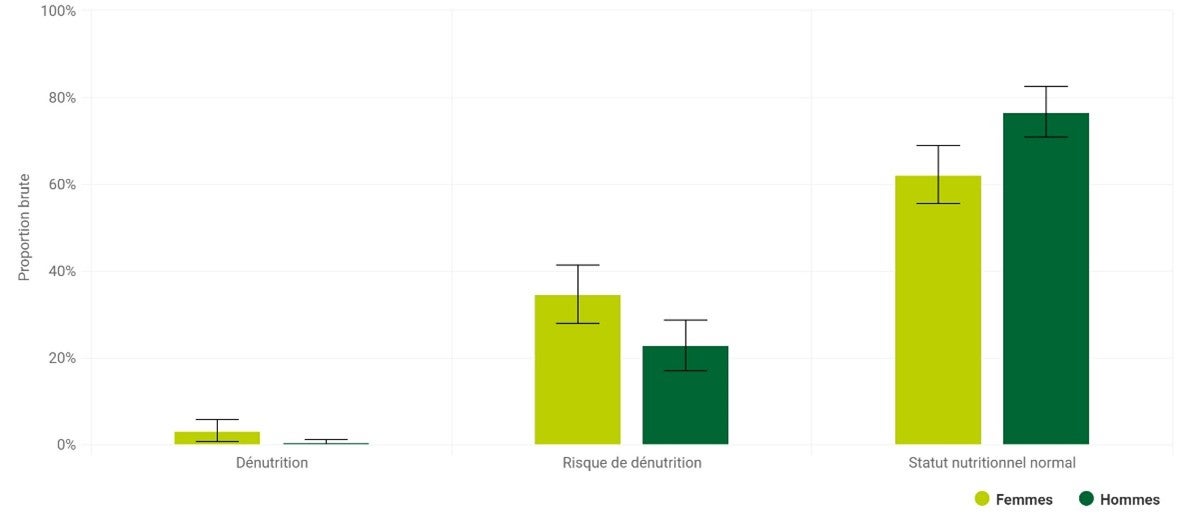
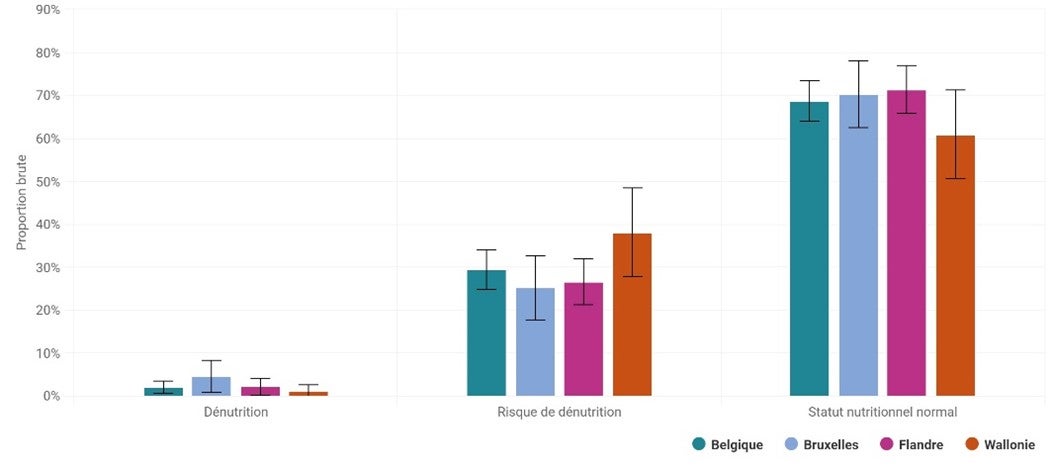
La dénutrition est un problème courant : on estime qu'entre 20 et 25 % des patients hospitalisés, soignés en institution ou soignés à domicile sont dénutris. Malheureusement, la dénutrition est loin d'être toujours reconnue comme telle, avec toutes ses conséquences. Nous savons tous depuis longtemps que le traitement de la dénutrition peut sauver des vies, mais saviez-vous qu'il permet également d'économiser de l'argent à court et à long terme ? Le traitement de la dénutrition est simple, efficace et économique ! Vous voulez en savoir plus ? Lisez l'article complet.
Le rapport "Dénutrition dans les soins : le traitement porte ses fruits", rédigé par Mark Nuijten et commandé par Eurocept Homecare, le Centre de connaissances sur la dénutrition, MediReva, Sorgente et l'Association des fabricants néerlandais d'aliments pour nourrissons et d'aliments diététiques (VNFKD), a été publié le 19 juin.
Contexte
On estime qu'entre 20 et 25 % des patients hospitalisés, soignés en institution ou soignés à domicile sont dénutris. Malheureusement, la plupart d'entre eux ne reçoivent pas le traitement nécessaire pour lutter contre la dénutrition, alors que le traitement en vaut la peine. En 2014, une étude économique similaire a été menée pour identifier les coûts sociaux de la dénutrition aux Pays-Bas. À l'époque, les coûts sociaux totaux de la dénutrition étaient estimés à 1,8 milliard d'euros par an. Comme beaucoup de choses ont changé en dix ans, une nouvelle analyse a été jugée nécessaire.
L'étude actuelle s'est fixé deux objectifs:
1. Déterminer le coût de la dénutrition non traitée aux Pays-Bas (en supposant des coûts de soins de santé en 2023).
2. Déterminer les coûts et les bénéfices du traitement de la dénutrition, en particulier le traitement diététique avec, si nécessaire, l'utilisation de la nutrition médicale orale, dans les hôpitaux et les établissements de santé (intra-muros) et à domicile (extra-muros, avec ou sans soins à domicile) en 2023.
Les principaux résultats peuvent être résumés comme suit :
• Les coûts médicaux directs de la dénutrition non traitée sont estimés à 3 milliards d'euros pour l'année de la dénutrition. Cela représente 3,4 % du total des coûts annuels des soins de santé aux Pays-Bas en 2023 !
• Le coût total de la dénutrition non traitée au cours de l'année d'apparition de la dénutrition est de 5,4 milliards d'euros, ce qui comprend : les coûts non médicaux, les coûts indirects liés à l'absentéisme au travail et le coût dû à la perte de QALYs (Quality Adjusted Life Years - c'est-à-dire le gain d'années de vie corrigées en fonction de la qualité de vie).
• Si une personne n'est pas traitée pour dénutrition pendant 5 ans, ces coûts peuvent atteindre 15,0 milliards d'euros.
• En termes de coûts et de bénéfices, les éléments suivants peuvent être résumés : les coûts de traitement de la dénutrition sont estimés à 360 millions d'euros. Les bénéfices associés aux coûts médicaux directs dus au traitement de la dénutrition sont calculés à 583 millions d'euros. Par conséquent, le traitement de la dénutrition entraîne une économie nette de coûts médicaux directs de 223 millions d'euros (583 millions d'euros - 360 millions d'euros). Si l'on ajoute les autres coûts de l'année de survenue de la dénutrition, on obtient même une économie nette de 749 millions d'euros (on pense aux économies de coûts non médicaux, à la baisse des coûts indirects de l'absentéisme et à la baisse des coûts due à la diminution de la perte de QALYs). Si l'on étend cette analyse à 5 ans, les économies nettes passent à 5,2 milliards d'euros !
• En traitant la dénutrition, les gens vivent plus longtemps, mais ces années de vie supplémentaires ont un coût. Pour mieux comprendre ce phénomène, l'efficacité du traitement de la dénutrition au cours d'une vie a également été examinée. Celle-ci a été calculée en divisant le coût supplémentaire net du traitement de la dénutrition, sans tenir compte des valeurs monétaires des QALYs, par le gain en QALYs. On obtient ainsi une valeur pour le coût par QALY ; pour le traitement de la dénutrition, cette valeur a été calculée à 15 552 euros. Aux Pays-Bas, on est prêt à dépenser de 20 000 à 80 000 euros par QALY, en fonction de la charge de morbidité. Avec un coût par QALY de 15 552 euros, le traitement de la dénutrition peut être considéré comme très efficace.
En bref :
• Chaque euro investi dans le traitement de la dénutrition rapporte 2,08 euros (749 millions d'euros / 360 millions d'euros) dans l'année de l'apparition de la dénutrition.
• Si l'on prolonge cette analyse sur 5 ans, chaque euro investi rapporte 14,44 euros (5,2 milliards d'euros / 360 millions d'euros).
En conclusion, le traitement de la dénutrition permet de réaliser des économies à court et à long terme.
Le rapport complet en anglais est disponible ici.
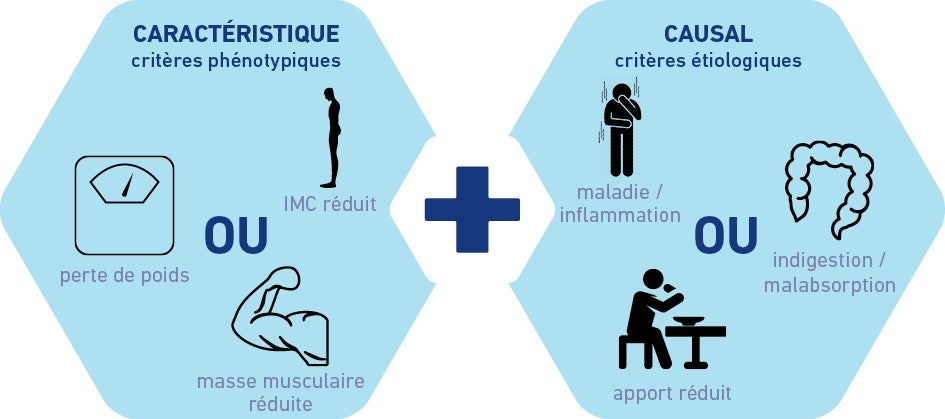
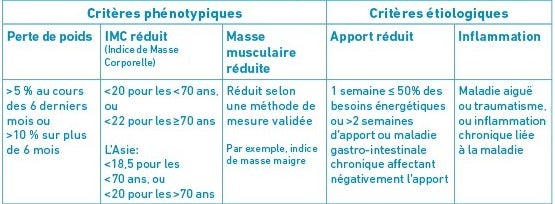
Saviez-vous qu'il existe également des outils de dépistage validés pour vérifier la malnutrition chez les personnes âgées ? Remplir le MNA complet prend 10 à 15 minutes. Cliquez ici pour voir le MNA.
Ce rapport a été rendu possible grâce au MNI GROW 6 de le « Medical Nutrition Industry » (MNI).
- En savoir plus sur Dénutrition dans les soins de santé
- Se connecter ou s'inscrire pour publier un commentaire